Loose Fuse Block Connections Are Stalling Engines and Making Them Hard to Start
- Certain GM generations have loose connections or broken wires inside the fuse bock.
- A disrution to electrical flow can cause intermittent flashing of warning lights or the engine to stall.
- The problem is often difficult to diagnose, leading some owners to pay for new batteries and starters before discovering the deeper cause.
This post originally appeared on chevroletproblems.com
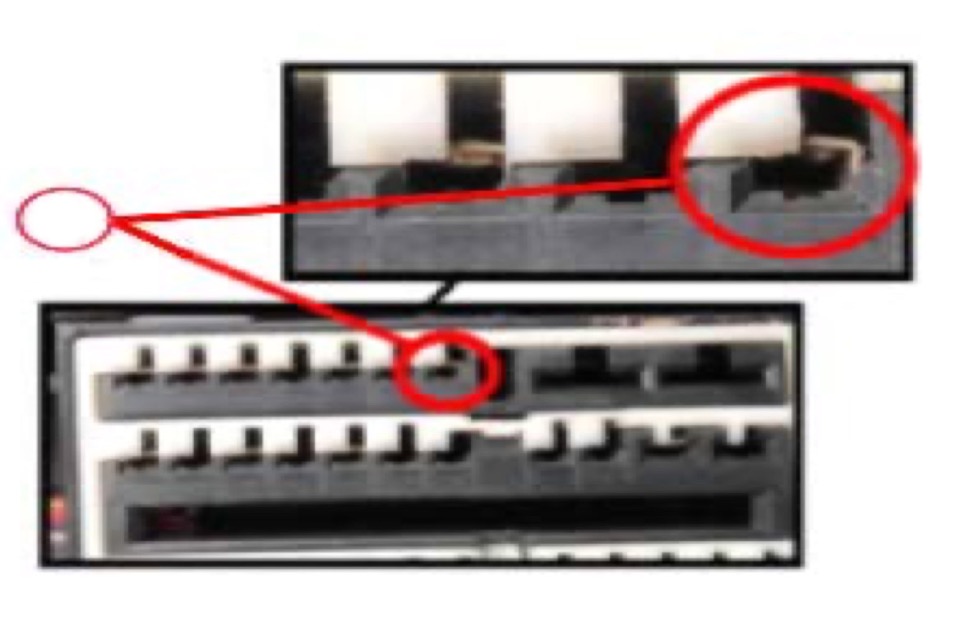
The fuse block (or box) distributes electrical energy from the battery system to different components throughout the vehicle. Inside a system of wires, fuses, and relays act as a gateway to control the flow of electricity.
Common GM Fuse Block Problems ∞
Certain generations of GM vehicles have problems inside the fuse block that cause flickering warning lights and stalled engines. Unfortunately these sorts of problems are often difficult to diagnose.
Loose relays disrupting the flow of electricity ∞
Relays plug into the fuse box sort of like how a power cord plugs into the wall of a home. In order for them to work, there needs to be enough tension to securely hold the relay's metal prongs in place.
But certain GM vehicles seem to have loose relays that can wiggle from vibrations in the road or engine. This will cause a temporary loss of electrical flow and will typically trigger the check engine, traction control, or reduced power warning lights along with diagnostic codes P1682 or P0689.
Depending on the relay and connection, the engine could also simply shut down while driving or idling.
Cracked wires stall a hot engine ∞
The copper wires carrying electrical current between the grounds, relays, and fuses inside the fuse block can crack. This provides a dead end for electrical flow and will cause the engine to stall.
In most cases you won't be able to restart the engine right away. That's because one of the copper wires that feeds electricity to the starter is routed in such a way that leaves it susceptible to heat, whether that's from a hot engine or a hot day.
Interestingly, owners find that their cold engines will crank but they'll stall out after about 30 minutes of the engine heating up.
GM Releases Service Bulletins About Loose Connections ∞
GM has released multiple technical service bulletins (TSB) about connection issues in the fuse block.
One of the latest is TSB #19NA276 regarding "customer concern of potential reduced engine power message displayed and/or engine stall with DTCs P1682 and/or P0689 set." The bulletin describes the cause as a poor terminal tension on terminal 51 in X50A Fuse Block - Under hood X3.
Technicians are advised to inspect terminal 51 for a loose connection, damage, or signs of burning and replace the fuse block with a new terminated lead if necessary.
Other bulletins talk about how tight-fitting terminals are imperative when a custom comes in complaining about reduced power or intermittent stalling.
TSB PIP5094 says it is imperative that all related terminal pin fit and tension be checked
when looking for circuit system issues in 2014 and prior GM models.
Similarly, TSB PIT5074M says [w]hen diagnosing an intermittent electrical concern terminal tension is one of the main culprits, especially when working with very small terminals
in 2005-2020 model years.
Fuse Block Lawsuit ∞
A class-action lawsuit alleged that the 2013-2017 Chevrolet Traverse, along with the 2013-2017 Buick Enclave and 2013-2017 GMC Acadia, are predisposed to electrical malfunctions that can cause stalled engines.
The plaintiff says a defective fuse block will cause intermittent or complete disruption of energy distribution, causing a vehicle not to start, intermittent stalling and other malfunctions. Metal prongs used with the terminals must be tight to prevent a loss of tension of the engine relay into the engine relay terminal.
The plaintiff used GM's TSBs as evidence, but the case was dismissed when the judge ruled the plaintiffs failed to tie their specific problems to terminal 51 which was referenced in one of the service bulletins.
Lawsuits Regarding This Problem
Lawsuits about this problem have already been filed in court. Many times these are class-action suits that look to cover a group of owners in a particular area. Click on the lawsuit for more information and to see if you're eligible to receive any potential settlements.
Dismissed Casey, et al., v. General Motors, LLC.
3:20-CV-00299Dismissed
A General Motors class action lawsuit has been dismissed after the owner of a 2014 Buick Enclave alleged a defective fuse block caused her SUV to suddenly lose power. The lawsuit says the fuse block terminals allegedly fail to maintain enough tension in these GM models.
Case Filed
A General Motors fuse block class action lawsuit alleges certain GM vehicles have problems with the tension of the terminals that can cause stalled engines and other electrical malfunctions.
Generations Where This Problem Has Been Reported
This problem has popped up in the following GMC generations.
Most years within a generation share the same parts and manufacturing process. You can also expect them to share the same problems. So while it may not be a problem in every year yet, it's worth looking out for.
1st Generation Acadia
- Years
- 2007–2016
- Reliability
- 32nd out of 32
- PainRank™
- 24.92
- Complaints
- 620